The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed how devices collect and share data, enabling automation across industries. But as systems grow more complex and real-time decision-making becomes essential, a new era is emerging: AIoT (Artificial Intelligence + IoT). This blog explores the key differences between Traditional IoT vs AIoT, highlights why AIoT is the future, and explains how businesses can adopt intelligent, autonomous systems for real-world impact.
What Is Traditional IoT?
Traditional IoT systems connect sensors, devices, and cloud services to collect and transmit data. They rely heavily on central servers for:
- Data processing
- Decision-making
- Analytics
- Storage
Key Characteristics of Traditional IoT
- Raw data collection: Devices capture sensor values and send everything to the cloud.
- High network dependency: Without internet, most IoT devices become limited or offline.
- Cloud-centric processing: Nearly all logic, analytics, and rules run in the cloud.
- Fixed behavior: Devices follow static rule-based logic.
- High bandwidth usage: Continuous transmission of raw data increases network load.
Traditional IoT works well for basic automation, dashboards, and monitoring — but struggles with latency, cost, and real-time intelligence.
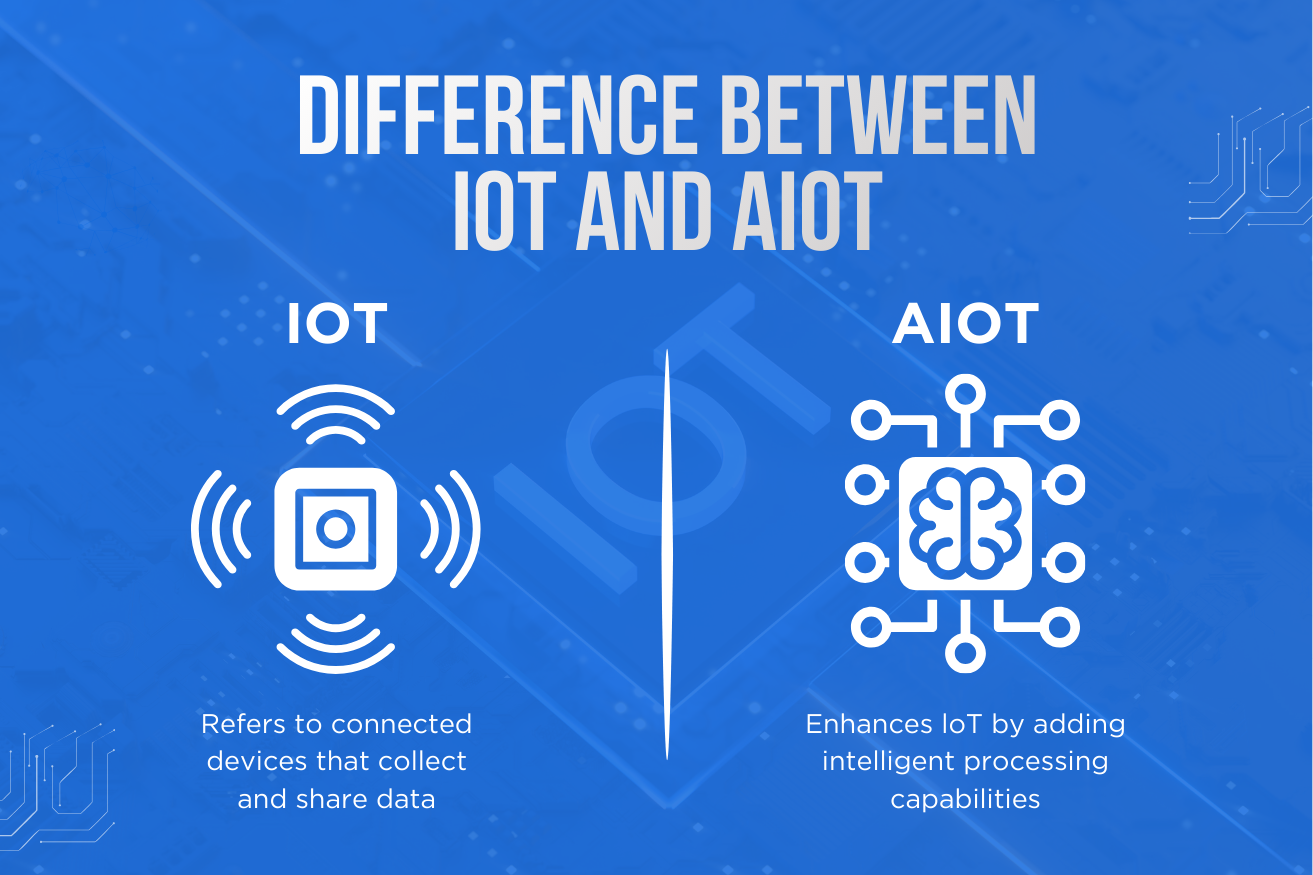
What Is AIoT? (Artificial Intelligence of Things)
AIoT integrates AI models, machine learning, and edge intelligence into IoT devices. Instead of simply sending data, AIoT systems can understand, predict, and act locally.
Key Characteristics of AIoT
- AI-driven interpretation: Devices don’t send raw data — they send insights.
- On-device processing: AI models run on microcontrollers, gateways, or edge nodes.
- Low-latency decisions: Immediate actions without waiting for the cloud.
- Adaptive logic: Devices learn the environment and improve over time.
- Low bandwidth usage: Only meaningful events or insights are pushed to the cloud.
- Autonomous operation: Works even during network outages.
Traditional IoT vs AIoT — A Detailed Comparison
- Data Collection
Traditional IoT: Collects raw sensor data only.
AIoT: Collects + interprets data instantly using embedded AI. - Data Transmission
Traditional IoT: Sends everything to the cloud.
AIoT: Sends only processed insights and anomalies. - Processing
Traditional IoT: Cloud-dependent, slower during high loads.
AIoT: Local edge processing with cloud as backup. - Decision-Making
Traditional IoT: Rule-based, limited adaptability.
AIoT: Dynamic, learning-based decisions. - Latency
Traditional IoT: High — depends on network roundtrips.
AIoT: Ultra-low — local decisions. - Reliability
Traditional IoT: Fails during connectivity loss.
AIoT: Operates offline independently. - Intelligence
Traditional IoT: No AI support.
AIoT: Supports TinyML, neural networks, anomaly detection. - Autonomy
Traditional IoT: Cloud-controlled.
AIoT: Acts independently.
Why AIoT Is the Future
- Faster responses for safety-critical systems
- Smarter automation across industries
- Reduced cloud dependency and cost
- Better privacy through local processing
- Scalable intelligence without overloading networks
Industries embracing AIoT:
- Manufacturing & IIoT
- Smart homes & buildings
- Smart cities
- Logistics & fleet automation
- Healthcare & wearables
- Agriculture & environmental monitoring
Real-World Use Cases of AIoT
- Smart Factories: AI-powered anomaly detection prevents downtime.
- Healthcare Devices: Wearables monitor vitals in real time and predict issues.
- Smart Cameras: Edge AI filters events and reduces false alarms.
- Predictive Maintenance: Machines forecast failures weeks early.
Traditional IoT vs AIoT — Which One Should You Choose?
Choose Traditional IoT for simple monitoring and dashboards.
Choose AIoT for real-time decisions, autonomy, and reduced cloud dependence.
Most modern systems benefit from a hybrid approach.
Final Thoughts
AIoT isn’t just the future — it’s already here. As industries push toward smarter, faster, and more autonomous systems, AIoT becomes essential for operational excellence and large-scale innovation. Companies that embrace AIoT today will lead the next decade of progress.