In today’s hyperconnected world, IoT sensors are the core building blocks enabling smart cities, intelligent manufacturing, connected healthcare, and data-driven decision systems. These sensors bridge the physical and digital worlds, capturing real-time information and turning it into insights that industries can act on.
Whether it’s monitoring soil moisture in agriculture, detecting vibration changes in factory motors, or powering adaptive lighting in cities — IoT sensors are reshaping how we observe, automate, and optimize environments.
What Are IoT Sensors?
IoT sensors are small, embedded devices that collect data such as temperature, humidity, motion, pressure, light, or location. This data is then transmitted over wired or wireless networks to cloud platforms or edge computing systems for processing and decision-making.
These sensors enable a real-time understanding of the environment — turning everyday objects into smart, interactive systems.
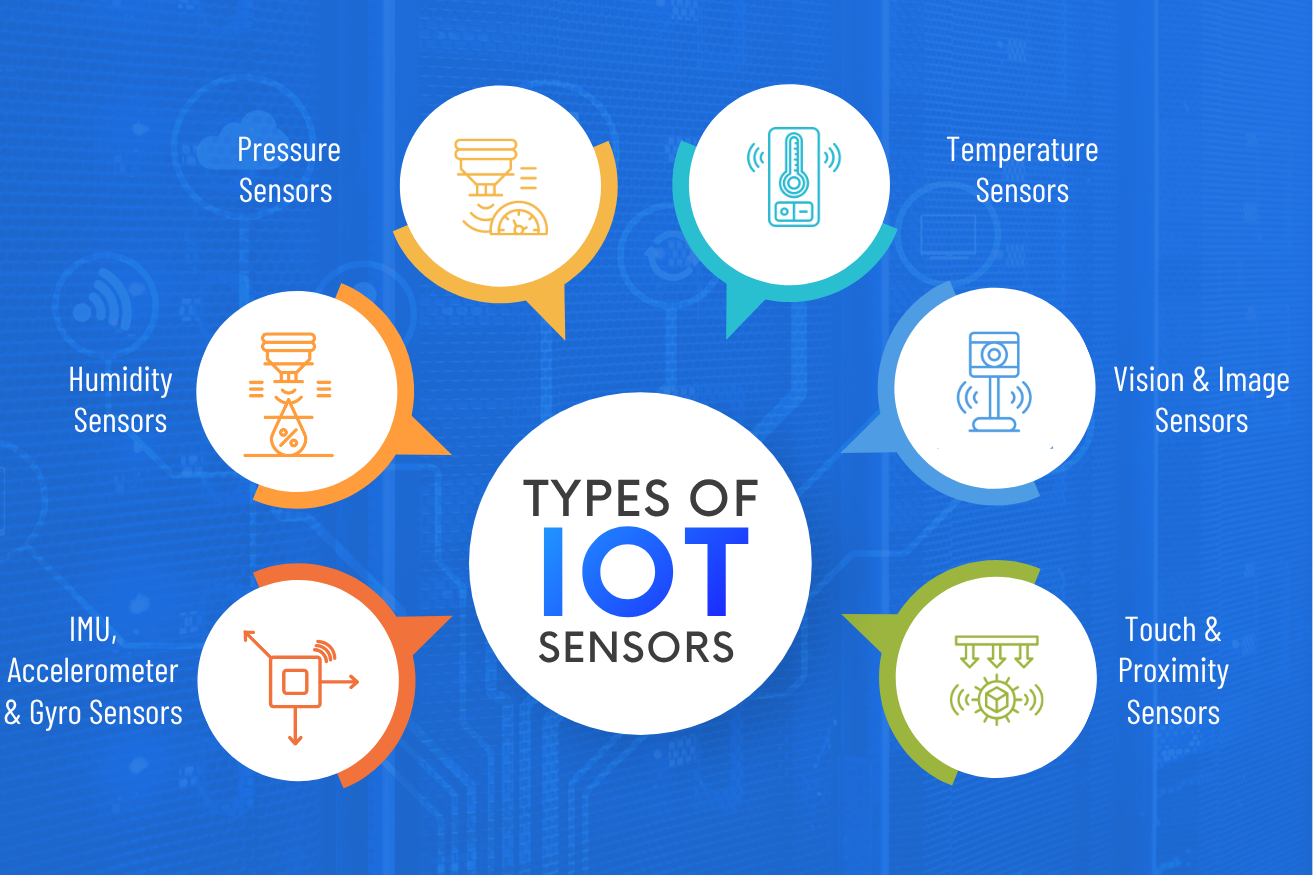
Types of IoT Sensors and Their Applications
1. Pressure Sensors
Used to measure force within fluids or gases.
- Industrial pipelines
- HVAC systems
- Water distribution networks
- Oil & gas infrastructure
2. Temperature Sensors
Maintain environmental and equipment temperature consistency.
- Cold-chain logistics
- Smart agriculture
- Industrial processing
- Smart buildings
3. Humidity Sensors
Track moisture in air or soil.
- Greenhouses
- Climate-controlled warehouses
- HVAC automation
- Healthcare facilities
4. Image (Vision) Sensors
Capture visual data for analysis and automation.
- Smart surveillance
- Robotics and automation
- Traffic monitoring
- Quality inspection in manufacturing
5. Inertial & Gyroscope Sensors
Measure motion, tilt, and orientation.
- Wearables and fitness devices
- Drones and autonomous vehicles
- Industrial machinery alignment
6. Touch & Proximity Sensors
Enable interaction and response.
- Consumer electronics
- Retail interactive displays
- Access control systems
IoT Sensor Connectivity: Wired vs Wireless
| Connectivity Type | Best For | Technologies Used |
|---|---|---|
| Wired IoT | High reliability environments | RS-485, CAN, Ethernet |
| Wireless IoT | Scalable, remote, flexible systems | Wi-Fi, BLE, LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, 5G |
Fast, secure communication ensures the sensor data can be acted on in real time.
IoT Sensors Across Industry Verticals
Commercial IoT
Smart buildings, healthcare monitoring, retail automation, office energy management.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Manufacturing, energy, logistics, oil & gas — where sensors detect anomalies, improve efficiency, and support predictive maintenance.
The Bigger Picture: Why IoT Sensors Matter
IoT sensors are not just about data collection — they enable:
- Predictive maintenance
- Real-time automation
- Energy efficiency
- Safety improvements
- Operational transparency
As industries move toward autonomous decision-making and AI at the edge, sensors provide the raw intelligence required for smarter systems.
Conclusion: The Future Is Sensing
IoT sensors are the foundation of digital transformation.
They enable environments to sense, react, and adapt — powering smarter cities, factories, and everyday life.
The future of IoT isn’t just about being connected — it’s about being aware.
And IoT sensors make that awareness possible.