Introduction
In the fast-growing world of IoT (Internet of Things) and embedded systems, one feature stands out as mission-critical: Over-the-Air (OTA) updates.
OTA updates allow manufacturers and developers to remotely update, patch, and improve firmware or software on devices after deployment. Instead of physically accessing each device, updates can be delivered wirelessly, saving time, reducing costs, and ensuring devices stay secure and functional.
From wearables and smart home products to industrial machines and connected healthcare devices, OTA has become the backbone of IoT lifecycle management.
Why OTA Updates Matter in IoT
OTA is more than convenience — it’s about:
- 🔒 Security – Apply urgent patches against vulnerabilities without recalling devices.
- ⚡ Scalability – Manage fleets of thousands of devices simultaneously.
- 💡 Feature Expansion – Add new functionalities post-deployment to extend product life.
- ⏱️ Reduced Downtime – Updates can be rolled out in the background with minimal disruption.
In industries like automotive, healthcare, and industrial IoT, OTA isn’t optional — it’s essential for compliance, safety, and competitiveness.
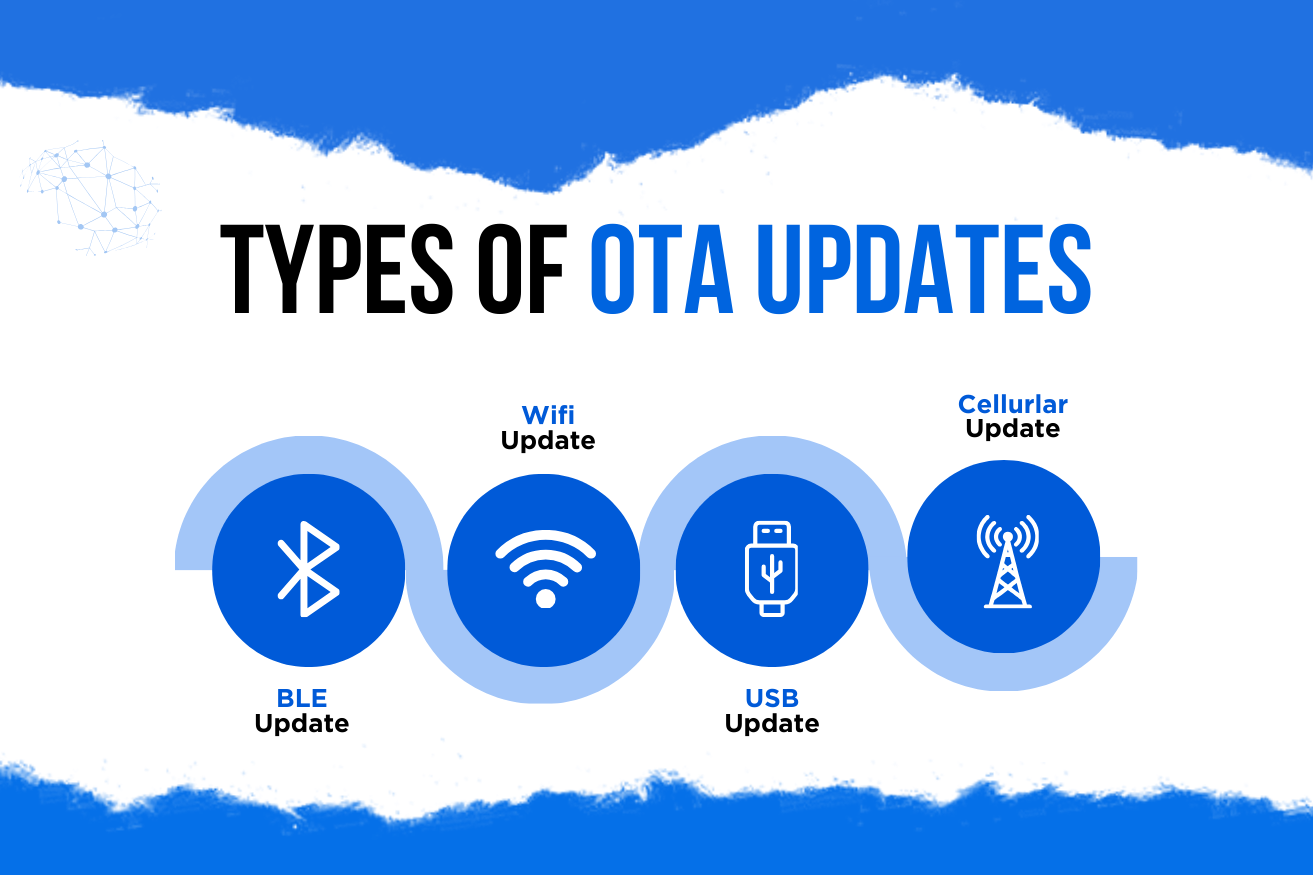
Types of OTA Update Methods
Different devices and environments call for different OTA methods. Here are the most common approaches:
🔹 BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) OTA Updates
- Use Case: Wearables, smartwatches, consumer gadgets.
- Advantages:
- Low power consumption (great for battery-operated devices).
- Simple setup using mobile apps as gateways.
- Limitations:
- Slower transfer speeds.
- Best for small firmware updates rather than large applications.
🔹 Wi-Fi OTA Updates
- Use Case: Home automation devices, consumer electronics, industrial IoT nodes.
- Advantages:
- Faster bandwidth supports complex updates and application bundles.
- Can leverage cloud platforms for large-scale rollouts.
- Limitations:
- Requires stable Wi-Fi connectivity.
- Power-hungry compared to BLE.
🔹 USB OTA (Local Firmware Update)
- Use Case: Industrial devices, gateways, or restricted environments.
- Advantages:
- High reliability, not dependent on network quality.
- Useful for factory flashing, debugging, or secure environments.
- Limitations:
- Not scalable for large deployments.
- Requires physical access.
🔹 Cellular OTA (4G/5G/NB-IoT)
- Use Case: Remote IoT devices such as agricultural sensors, EV charging stations, fleet management units.
- Advantages:
- Global coverage and scalability.
- Ideal for devices that are mobile or in remote locations.
- Limitations:
- Higher operational costs due to SIM/data usage.
- Requires optimized update mechanisms to reduce bandwidth use.
Security in OTA Updates
OTA can be a double-edged sword if not implemented securely. A compromised update pipeline could allow attackers to push malicious firmware. Best practices include:
- ✅ Code Signing – Only run firmware signed by trusted private keys.
- ✅ Encryption – Protect data transfer with TLS/SSL to prevent interception.
- ✅ Rollback Mechanism – Ensure devices can revert to a safe version if an update fails.
- ✅ Delta Updates – Send only changes (diffs) instead of full firmware to save bandwidth.
Best Practices for Implementing OTA
- Segment Rollouts – Update a small batch first, then expand once stable.
- Optimize Firmware Size – Use compression and modular updates to reduce overhead.
- Test in Simulated Environments – Validate updates in lab conditions before field deployment.
- Monitor After Update – Use telemetry to confirm device health and performance.
- Plan for Failures – Always include recovery mechanisms like dual-partition firmware.
MetaDesk Global and OTA Solutions
At MetaDesk Global, we’ve implemented OTA across projects built on:
- ESP32 – Secure BLE + Wi-Fi OTA for consumer devices.
- STM32 – Industrial-grade OTA with USB and cellular backup.
- nRF52 – Ultra-low-power BLE OTA for wearables and health devices.
By combining secure firmware pipelines with cloud integration, we help our clients deliver devices that remain secure, scalable, and future-ready long after deployment.
Conclusion
OTA updates are no longer a “nice-to-have” feature in IoT — they’re a must-have. From security patches to new feature rollouts, OTA ensures devices remain relevant, reliable, and competitive.
💡 Whether through BLE, Wi-Fi, USB, or cellular, the right OTA strategy can define the success of your product.
At MetaDesk Global, we specialize in building OTA-enabled IoT solutions tailored to your hardware platform and deployment scale.